Collins-Modoc Reforestation
The Groundbreaking Reforestation Project in the American West
RENEWWEST HELPS BREAK GROUND ON THE LARGEST REFORESTATION CARBON PROJECT IN US HISTORY.
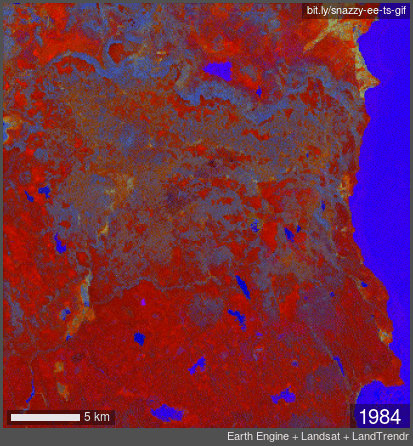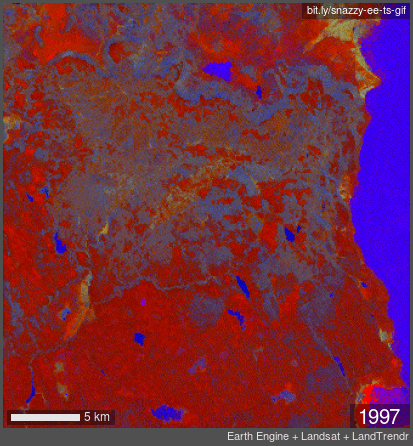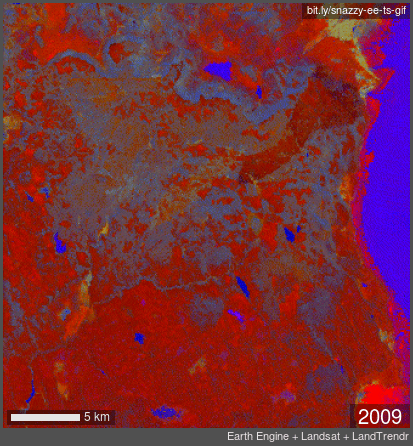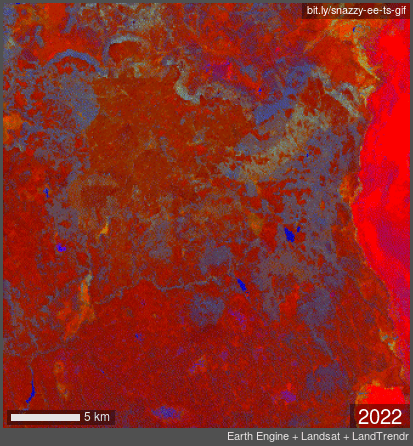
In 2012, the large Barry Point Fire hit 92,977 acres of forest in Northern California. Over 7 years later, the forests had made no sign of recovery naturally. Without human planting, the land would not recover.
RenewWest stepped in to partner with one of the larger landowners in this area of California to help reestablish a sustainably managed forest. As a result of the $3.4m generated by RenewWest, the landowner was able to replant 2.5 million seedlings across nearly 9,962 acres, a single site record in the United States for a carbon-focused project, breaking ground for large-scale reforestation in the United States.
fast facts
Largest reforestation carbon project in US history (single-site)
9,962 acres
2.5 million trees
1,310,760 metric tonnes CO2e captured over 100 years
Reestablishes habitat for native species
Perpetual Conservation Easement with Habitat Enhancement Plan
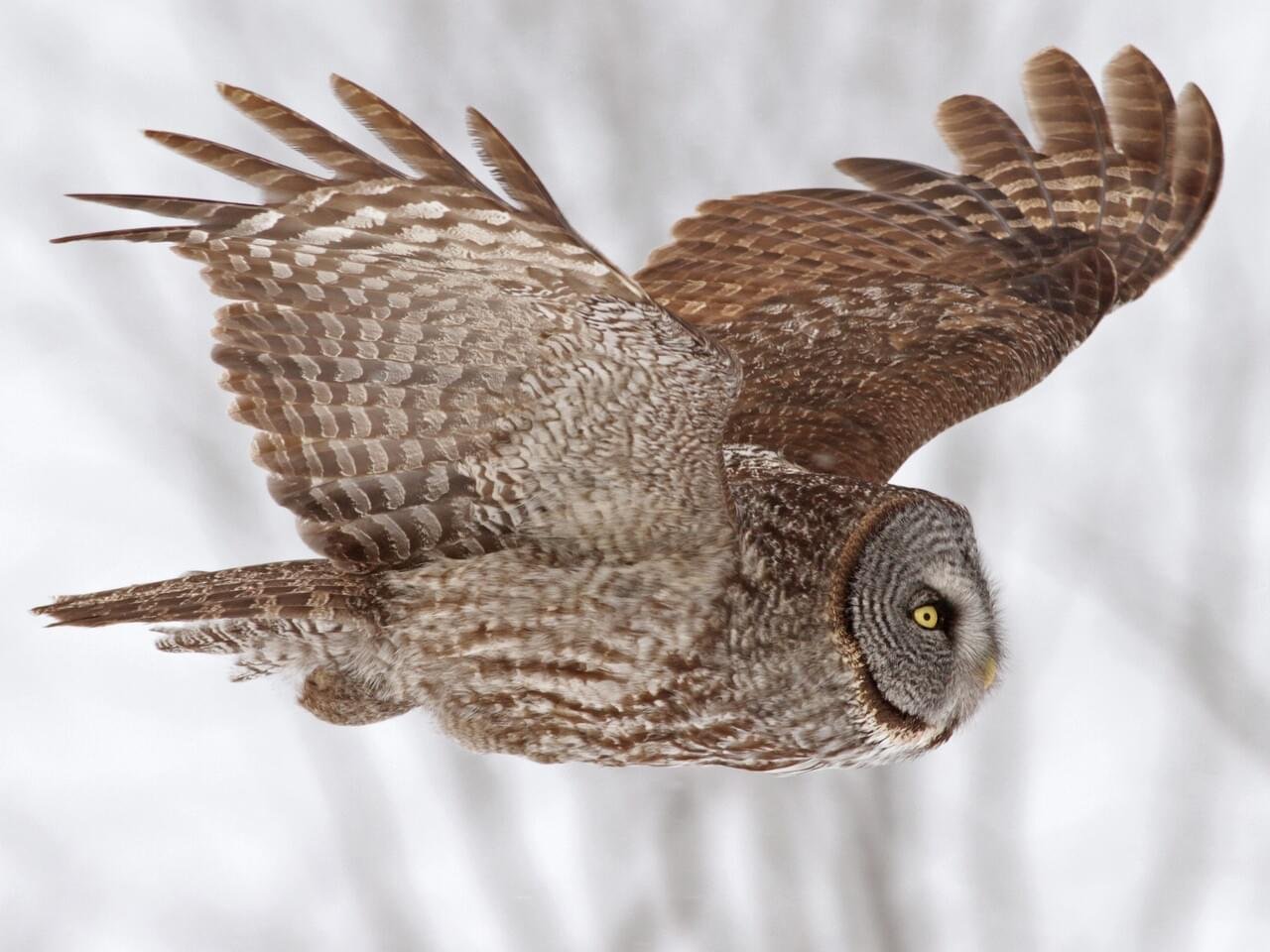
Monitor for Great Gray Owl, a California Endangered Species
Improves water temperature, quality, watershed recharge
Project type
ARR under Compliance ARB Forest Protocol
Eligible for VCM through Climate Action Reserve Forest Protocol V.4
theory of change
The Collins Modoc Reforestation Project is located on the Modoc Plateau, west of Goose Lake and surrounded by the Modoc National Forest.
This area was once a dynamic forest, but after the fire the land failed to naturally regenerate. Environmental assessments suggested this would lead to negative environmental outcomes in runoff, erosion, habitat, and decreased natural beauty for the surrounding communities.
By reforesting, the risks are mitigated. Water outcomes will improve, critical habitats will be restored, and the new trees will generate a fast-growing carbon sink.
TIME LAPSE: false color infrared Landsat imagery showing years 1989 through 2020. Note fire and forest loss in 2013 with the transition from grey to orange.
ecosystem value creation
A qualified hydrological assessment was performed of the site by Pranesh Selvendiran, PhD of LimnoTech. According to the report, the Water Quality Benefit of 3,410 liters per year of reduced runoff and increased recharge would be achieved.
A Water Quality Benefit of 4,778 metric tons per year reduced erosion, providing real water benefit to the Pit and Klamath watersheds.
Restoration will provide priority habitat for dozens of species. Prior to the fire the properties mosaic of meadows, riparian woodlands and aspen grove, mountain mahogany savanna, low sage and eastside pine stands provided a unique habitat complex identified by the California Wildlife Action Plan as deserving additional protection. These adverse habitat types support a number of special status species such as greater sandhill crane, great gray owl, goshawk, Bald eagle and black backed woodpecker as well as 25 rare plants.
The land, once restored, will have a diversity of habitat types, including conifer forest, meadows, in-stream and wetland attributes, aspen groves, juniper and sagebrush.
The project directly and indirectly impacts habitats of threatened and endangered species, species that are candidates for listing under state or federal statutes, rare species and other species important to the state, such as deer and elk are enhanced by this project
This product is consistent with the express goals of the US Endangered Species Act of 1973 and the California Endangered Species Act of 1984.
HABITAT CONNECTIVITY: this project provides critical habitat connectivity for wildlife between the two adjacent National Forests, Modoc National Forest in California and Fremont-Winema National Forest in Oregon.
Several state and federal wildlife areas are within the vicinity of a project area. The Modoc National Wildlife Refuge is 33 air miles to the southeast, and Clear Lake National Wildlife Refuge is 24 air miles to the southwest.
BIRD MIGRATION:The property is located within the boundaries of the Pacific Flyway, an Audubon priority flyway that creates habitats for at least a billion migrating birds each year, and creates connectivity from the Upper and Lower Chewaucan Marsh, Malheur National Wildlife Refuge, and the Modoc National Wildlife Refuge. Learn more about the Pacific Flyway
As part of the Special Habitat Management Zone designation, there is an established partnership with the California Dept of Fish and Wildlife to monitor and measure the enhancements to habitat through the Habitat Enhancement Plan, including great gray owls, a California Endangered species. The harvesting of trees is one of the greatest threats this species faces.



climate change mitigation
The primary objective of the project is reestablishing high-value carbon sinks, including trees, vegetation, and improved soil organic carbon.
The project will sequester 1,310,760 tonnes of CO2 in the trees over 100 years.
project impact areas
ECONOMIC
First project to unlock funding into large-scale reforestation
ECOLOGICAL
Reestablishes conifer forest.
Improves biodiversity compared to baseline.
Improves habitat for endangered and threatened species.
WATER
Measured benefits for watershed recharge
Reduces erosion
Great gray owl, a California Endangered species. The harvesting of trees is one of the greatest threats this species faces.
sustainable development goals alignment
GOAL 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
GOAL 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
GOAL 13: Climate Action
GOAL 15: Life on Land
GOAL 17: Partnerships
assurance + ADDITIONALITY
INDEPENDENT VERIFICATION
Compliance ARB Forest Protocol
Designed to meet & eligible for VCM CAR Forest Protocol V.4
Project ID: CAR1487
First Verification: Ruby Canyon Engineering, scheduled for May 2023
BUFFER POOL
15.87% of the credits have been allocated to a buffer pool
WHAT IS A BUFFER POOL?
Buffer pools are designed to safeguard previously issued carbon credits. They act as an insurance pool of unused credits, such that in the case of a reversal or other error, there are still climate mitigation credits to compensate for the loss. For example, if a carbon offset project claims to remove 50,000 tons of carbon per year, the project might donate 10,000 of those tons to the pool, making them unavailable for trading on voluntary carbon markets. This insurance payment creates a large shared pool of ‘spare’ carbon credits across the world, which protect participating projects against future worst-case scenarios. If a forestry project in Tanzania burns down, credits can be drawn from the pool — which might consist of credits from all over the world — to make up for the loss. Learn more about Buffer Pools from Sylvera.
LONG TERM MANAGEMENT
The landowner is an experienced forest manager and established a 100-year management plan.
Management plan includes multi-age thinning to enhance forest health and regeneration.
A Habitat Enhancement Plan is included with the Conservation Easement and includes management plans for grazing, forests, and wetland.
Designation of Special Habitat Management Zones (SHMZs).
ADDITIONALITY TEST
The credits generated by this project yield a surplus of GHG emissions reductions or removal enhancements exceeding those otherwise required by law or regulation or a conservative business-as-usual scenario.
In addition, the area showed no natural regeneration after 7 years.
WHAT IS ADDITIONALITY?
A key principle of carbon finance. Did the project improve something, or would the land have looked the same without it? Checking for additionality demonstrates whether the project is justified, if it avoided deforestation or somehow preserved carbon storage. Additionality is usually measured through scientifically-designed modules as a part of the independent verification process by organizations like Verra, Climate Action Reserve, and Gold Standard.
baseline comparison
The tree growth analysis estimates that 1,310,760 metric tonnes of CO2 will be captured above 100 year baseline.
Remote and on-site sampling is performed to estimate pre-existing tree canopy cover and natural regeneration occurring irrespective of the project activity, respectively.
What is Baseline? Baseline is the “business as usual” case for reforestation projects. As only newly established trees are being assessed as the primary effect of a project, with future sequestration being impacted by the presence of older, pre-existing trees or naturally regenerating trees that would have been present regardless of whether the project activity was undertaken, such trees competing for resources and canopy area with those trees established by the project are included in the baseline. Baseline carbon stocks are evaluated based on an estimate of canopy cover of preexisting trees and/or an estimate of natural regeneration occurring irrespective of the project activity.
durability
100 years
Property includes a 100 Year Management Plan
The property is placed in a conservation easement, a legal structure that runs with the land title, that provides enforceable restrictions.
The conservation easement is held by the Pacific Forest Trust
WHAT IS DURABILITY?
Durability is another key issue in carbon finance. It describes the planned duration of storage and the degree of confidence that a particular project will actually keep carbon out of the atmosphere for a given period of time. In addition to strategic approaches to project design and implementation, there is a mechanism at work behind the scenes of carbon programs, and it’s designed to ensure permanence. It works by ‘allocating’ a certain number of credits to a central ‘buffer pool’ of carbon credits. See ‘Buffer Pool’ above to learn more.
A reforested stand planted several years before showing success rates.